For spreadsheets created in Microsoft Excel 365, check the following accessibility guidelines for each document element to make sure that your document is accessible.
Make Text Accessible
Use a text font that is easy to read
- Ensure your text is readable by using a sans serif fonts, such as Arial, Helvetica, or Verdana, that is at least 10pt in size. These font settings will magnify well for those who have low vision.
- If there is an image that includes text, make sure to repeat that text in the alternative text field for the image so it will be accessible to assistive technology users.
- Refrain from using floating text boxes, track changes, or commenting - these features are not accessible.
Make Images and Graphics (including Graphs, Maps, and Shapes) Accessible
Provide alternative text descriptions (alt text) for images and graphics.
Alternative text descriptions of images (alt text) allow screen reader users to benefit from the information being conveyed by an image.
- Right-click on the image and select Edit Alt Text.
- The Alt Text Pane will open on the right side of the spreadsheet.
- In the field provided, type descriptive text about the image.
Make Links Accessible
Write meaningful link text that indicates the link's destination
Links are a major method of navigating for everyone, but especially screen reader users. If the links are embedded into meaningful text, they are much more useful.
- Select the cell that describes the destination of the link.
- Right-click and select Link.
- In the Address field, type the link URL.
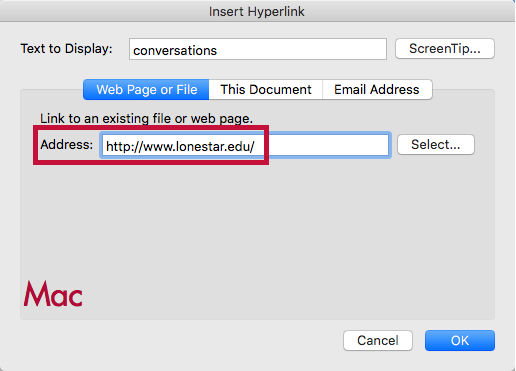
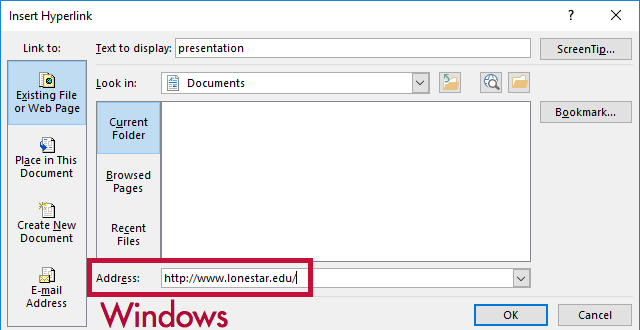
- Click OK.
- If you think students will be printing the document and you want them to have the URL, put it in parentheses after the link but don't hyperlink it.
- Example: Lone Star College (www.lonestar.edu).
- Screen reading software can pull up all of the links in a page to aid the user in navigating the page more quickly. If a link pulled up by the screen reader is an indecipherable URL or an ambiguous phrase like "click here," the user will not know where that link goes.
Make Tables Accessible
Create data tables with column headers
Designating column or row headers in a table is essential for screen reader users to understand how the information is laid out.
Windows:
- Place the cursor anywhere in a table.
- On the Table Tools Design tab, in the Table Style Options group, select the Header Row check box.
- Type the column headings.
Mac:
- Place the cursor anywhere in a table.
- On the Table tab, select the Header Row check box.
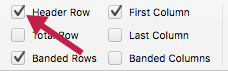
- Type the column headings.
Ensure a proper reading order in tables
- Screen readers read tables from left to right, top to bottom, one cell at a time (no repeats). If cells are split or merged, the reading order can be thrown off.
- To test the reading order of your table, place your cursor in the first cell of the table. Press the Tab key repeatedly to navigate through the table. This demonstrates the reading order that assistive technologies will use.
- Merged, nested, and split cells change the reading order of tables. Make sure you construct your table in a way that accommodates proper reading order.
Makes Sheets Accessible
Give all sheet tabs unique names
Screen readers read sheet names, which provide information about what is found on the worksheet, making it easier to understand the contents of a workbook and to navigate through it.
- Right-click a sheet tab, and select Rename.
- Type a brief, unique name for the sheet.
Color Use in Documents
Don't use color alone to convey meaning
Don't use color alone to make a distinction, to make a comparison, or to set something apart from the rest of the document. If you categorize something by color alone, those who are color blind or have other visual disabilities will not be able to benefit from that information.
Use sufficient color contrast
Make sure there is enough contrast between the font color and the background color. If you print your document on a black and white printer, would it be understandable? Without sufficient color contrast, people who are color blind or have other visual disabilities will not be able to benefit from that information. You can use the Colour Contrast Analyzer tool to help you verify that the color contrast in your document is sufficient.
How To Install and Use the Colour Analyzer tool
- Download Colour Contrast Analyzer Tool
- Open the Colour_Contrast_Analyzer application
- Make sure you are in the Result -- Luminosity mode, not the contrast result for color blindness.
- Click the Foreground eye dropper tool, hover over and click the foreground color to select it.
- Click the Background eye dropper tool, hover over and click the background color.
- If you have a 12-pixel font color you are testing for color contrast, you must get a Pass (AA).
If you have font larger than that, you must get a Pass (AA) in the Large Text field.
- LSC's standards are to reach a pass in the AA standards.
- Don't worry If you fail the AAA standards, though you might want to consider something with more contrast.
![]() Video: How to use the Colour Contrast Analyzer tool.
Video: How to use the Colour Contrast Analyzer tool.
Make Math and Science Equations Accessible
Math and Science Equations
Mathematical equations and scientific notations must be written with MathType (an Microsoft Office equation editor plugin) and saved in a source folder in your course files. This enables Disability Services to access those files and convert them to an accessible format for a visually impaired student.
For more information, see How to Make Math-Science Resources Accessible.
Run the Built-In Accessibility Checker
Windows:
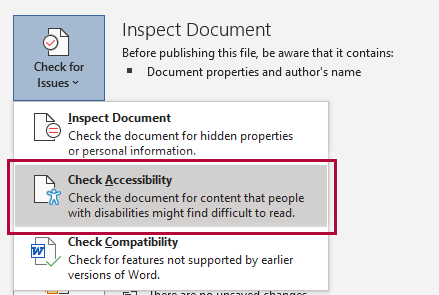
- Go to the File tab.
- Select Info from the sidebar menu.
- Click the Check for Issues button.
- Select Check Accessibility from the drop-down list.
Macs:
- Click Tools.
- Click Check Accessibility.
The Accessibility Checker panel will open to the right of the spreadsheet. The accessibility checker provides you with a list of errors, warnings, and tips. When you click on an error or warning, instructions on how to fix it appear below the list of errors, in "Additional Information."



